What Is The Purpose Of A Nonrepudiation Service In Secure Communications?
What is nonrepudiation?
Nonrepudiation ensures that no party can deny that information technology sent or received a message via encryption and/or digital signatures or approved some information. It also cannot deny the authenticity of its signature on a certificate.
Although information technology originated every bit a legal concept, nonrepudiation is besides widely used in computing, information security and communications.
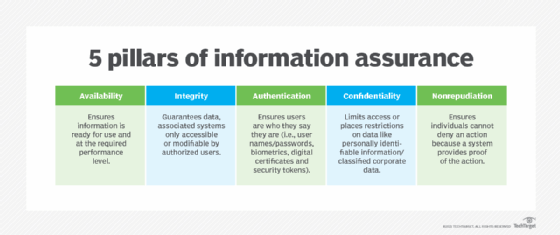
Information assurance and nonrepudiation
Nonrepudiation is one of the five pillars of information balls (IA), which is the do of managing information-related risks and protecting information systems, like computers, servers and enterprise networks. The other four pillars are the following:
- integrity
- availability
- authentication
- confidentiality
Nonrepudiation provides proof of the origin, actuality and integrity of information. Information technology provides assurance to the sender that its message was delivered, every bit well equally proof of the sender's identity to the recipient. This way, neither political party can deny that a bulletin was sent, received and processed.
Nonrepudiation is like authentication, particularly with respect to implementation. For instance, a public cardinal signature tin can be a nonrepudiation device if only 1 political party can produce signatures.
In general, nonrepudiation combines both authentication and integrity.
Nonrepudiation, message authentication code and digital signatures
Nonrepudiation is achieved through cryptography, similar digital signatures, and includes other services for authentication, auditing and logging.
In online transactions, digital signatures ensure that a political party cannot later deny sending data or deny the authenticity of its signature. A digital signature is created using the private primal of an asymmetric primal pair, which is public key cryptography, and verified with a corresponding public central.
Just the individual key holder tin can access this key and create this signature, proving that a document was electronically signed by that holder. This ensures that a person cannot afterwards deny that they furnished the signature, providing nonrepudiation.
In cryptography, a message authentication code (MAC), also known as a tag, is used to cosign a message or confirm that the message came from the stated sender and was not changed along the way. Different digital signatures, MAC values are generated and verified using the aforementioned secret key, which the sender and recipient must agree on before initiating communications.
A MAC can protect confronting bulletin forgery by anyone who doesn't know the shared cloak-and-dagger key, providing both integrity and authentication. Nevertheless, MAC algorithms, like cipher-based MAC and hash-based MAC, cannot provide nonrepudiation.
In addition to digital signatures, nonrepudiation is also used in digital contracts and electronic mail. Email nonrepudiation involves methods such as electronic mail tracking.
Drawbacks of nonrepudiation with digital signatures
Since no security technology is foolproof, some experts warn that a digital signature solitary may non always guarantee nonrepudiation. Some suggest using multiple approaches to ensure nonrepudiation. One such practice is to capture biometric information and other information about the sender or signer that collectively would be difficult to repudiate.
It'south likewise important to know that the current definitions of nonrepudiation in the digital infinite consider only the validity of the signature itself. They practice not allow for the possibility that the signer was manipulated, forced or tricked into signing. It'due south too feasible that a virus, worm or other type of malware can compromise a sender's individual central, mayhap stealing or forging its digital signature and jeopardizing nonrepudiation.
To avoid such issues and to ensure that a digital signature is valid -- and, therefore, the advisable choice for nonrepudiation -- it must be established through a secure and fully trusted document handling and signature mechanism.
Another concern is the possibility that a digital signature remains the same, even if it's been faked by someone who has the private key. The U.S. Department of Defense force addressed this problem with the mutual access menu (CAC), a type of smart menu for agile duty defense force personnel.
The CAC proves the holder's identity and enables physical access to controlled spaces and defense force computer systems. It satisfies the requirements for digital signatures, also as three IA pillars: nonrepudiation, integrity and hallmark.
This was last updated in August 2021
Go on Reading About nonrepudiation
- 8 electronic signature all-time practices to build in to your workflow
- When should you employ an electronic signature vs. digital signature?
- Biometric security technology could come across growth in 2021
- Integrating security with robotic process automation
- Cryptography nuts: Symmetric key encryption algorithms
Dig Deeper on Identity and access management
-

common authentication
-

Digital Signature Standard (DSS)
-

Secure Electronic Transaction (Ready)
-

asymmetric cryptography (public key cryptography)
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/nonrepudiation
Posted by: lamarchetwoment.blogspot.com





0 Response to "What Is The Purpose Of A Nonrepudiation Service In Secure Communications?"
Post a Comment